GA4 Attribution for SEO simplifies how you measure organic search's role in conversions. Instead of just crediting the last-click source, GA4 spreads credit across all touchpoints in your customer's journey. This means you can see how SEO contributes to early discovery, mid-funnel engagement, and final conversions.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- GA4 Attribution Models: Data-Driven Attribution (DDA) uses machine learning to assign credit to every interaction, while rule-based models like Last Click focus on the final touchpoint.
- Why It Matters for SEO: Understand how organic search drives brand awareness and conversions, even if it's not the last step.
- How to Set It Up: Choose the right model, configure settings, and mark key SEO events to track performance.
- Search Console Integration: Combine search query insights with GA4 data for a complete view of your SEO impact.
Key Tip: Use GA4's Model Comparison Tool to see how different attribution models affect your organic search data. This helps you choose the best setup for your strategy.
Attribution Modelling and Reporting in GA4 Explained
sbb-itb-5be333f
Attribution Models in GA4
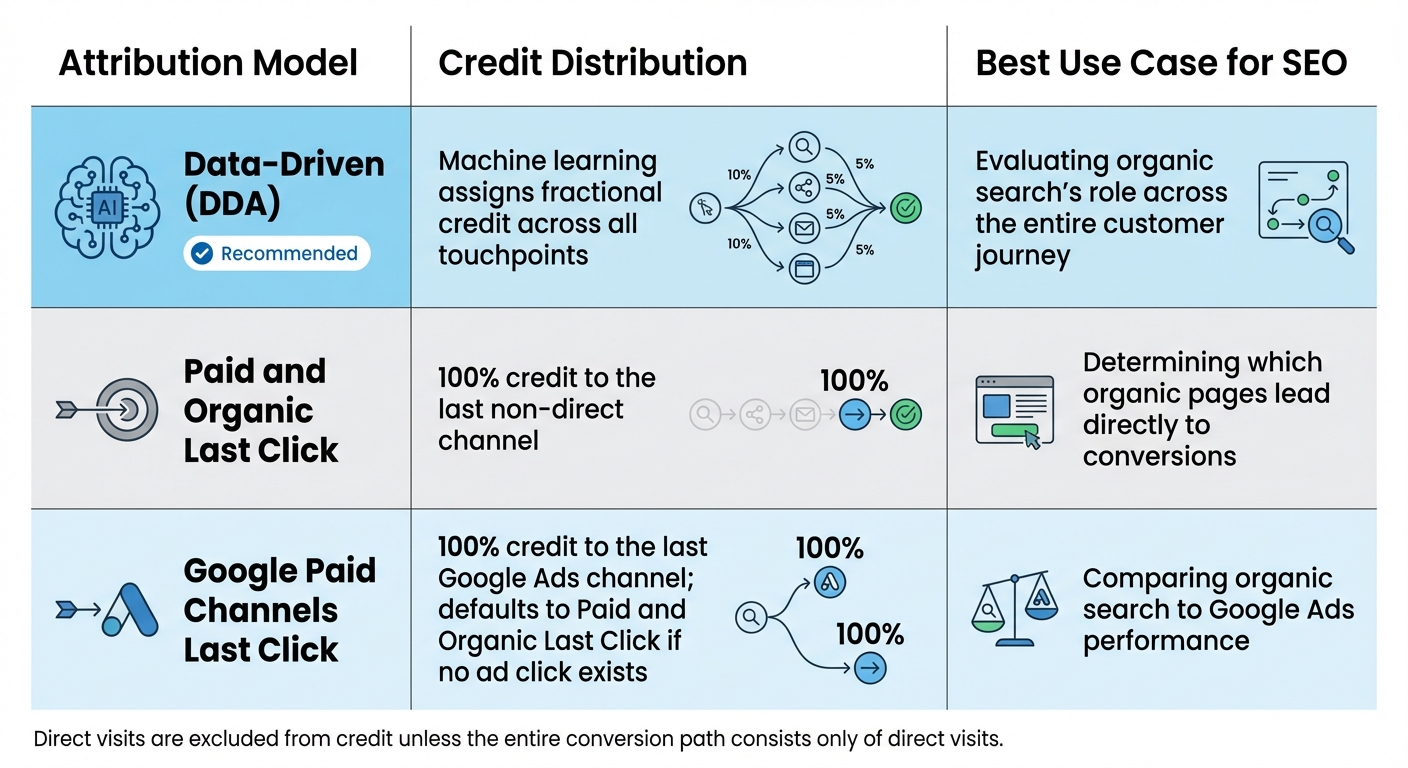
GA4 Attribution Models Comparison for SEO
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) offers two main attribution models: Data-Driven Attribution (DDA) and a couple of rule-based options. Back in November 2023, GA4 retired several rule-based models, leaving DDA and two last-click variations as the only choices. Understanding how these models work is essential for setting up effective SEO tracking in GA4 using top SEO tools.
Data-Driven Attribution Model
The Data-Driven Attribution (DDA) model is the default for all new GA4 properties. It relies on machine learning to analyze user behavior, examining both converting and non-converting paths. By studying historical data, it evaluates how much influence each touchpoint - like an organic search visit - had on the final conversion.
This model is particularly helpful for SEO because organic search often plays a vital role early in the customer journey. For example, a user might first find your site through a Google search, later engage through an email campaign, and eventually convert after a direct visit. DDA assigns fractional credit to each interaction, giving you a more complete picture of how every channel contributes to the overall journey - not just the one that closed the sale.
DDA also has a dynamic feature: it can reassign conversion credit up to 7 days after the event, adjusting as new touchpoints are identified.
Rule-Based Attribution Models
GA4 now includes only two rule-based attribution models: Paid and Organic Last Click and Google Paid Channels Last Click. These models use fixed rules to assign credit.
- Paid and Organic Last Click: Also called "last non-direct click", this model gives 100% of the credit to the last non-direct channel. For instance, if a user discovers your site through organic search and later returns directly to make a purchase, the credit goes entirely to organic search.
- Google Paid Channels Last Click: With this model, 100% of the credit is assigned to the last Google Ads channel a user interacted with. If no ad click exists, it defaults to the Paid and Organic Last Click model. This is especially useful for comparing organic search performance to Google Ads campaigns.
While these last-click models can help pinpoint specific interactions, they don’t account for earlier touchpoints in the customer journey. This limitation makes them less effective for understanding SEO’s role in multi-touch scenarios, especially compared to the broader perspective offered by DDA.
| Attribution Model | Credit Distribution | Best Use Case for SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Data-Driven (DDA) | Machine learning assigns fractional credit | Evaluating organic search's role across the entire journey |
| Paid and Organic Last Click | 100% credit to the last non-direct channel | Determining which organic pages lead directly to conversions |
| Google Paid Channels Last Click | 100% credit to the last Google Ads channel; defaults to Paid and Organic Last Click if no ad click exists | Comparing organic search to Google Ads performance |
One important note: GA4 excludes direct visits from receiving credit unless the entire conversion path consists only of direct visits. Up next, we’ll dive into how to configure these attribution settings for your SEO campaigns.
How to Set Up Attribution for SEO in GA4
Setting up attribution in GA4 involves selecting the right model, configuring settings, and marking key SEO events. This ensures that every organic interaction gets the credit it deserves, showcasing SEO's impact throughout the customer journey.
Accessing Attribution Settings
To adjust your attribution settings in GA4, head to Admin, then under Data display, click Events and select Attribution settings. Keep in mind, you’ll need a Marketer role or higher at the property level to make these adjustments.
The Reporting Attribution Model determines how credit is applied across your GA4 reports. Any changes you make here will apply retroactively to both historical and future data. For SEO tracking, make sure the "Channels that can receive credit" option is set to Paid and organic channels for a comprehensive view across all touchpoints.
You’ll also encounter lookback windows, which define how far back a touchpoint can receive credit. By default, GA4 uses 30 days for acquisition conversion events (like first_open and first_visit) and 90 days for other conversion events. These defaults are well-suited for typical organic search behavior. Once these settings are in place, you can move on to selecting the attribution model that aligns with your SEO strategy.
Choosing the Right Attribution Model
For SEO, Data-Driven Attribution is often the best choice. It uses machine learning to allocate credit across all touchpoints in a user’s journey.
Before committing to a new model, take advantage of the Model Comparison Tool in GA4. You can find it under Advertising > Attribution > Model Comparison. This tool lets you preview how different attribution models might redistribute credit across your organic channels without making permanent changes. For instance, if you’re currently using Last Click, you can see how switching to Data-Driven Attribution would alter your conversion data.
When using Data-Driven Attribution, you might notice fractional numbers (e.g., 0.5 conversions) in your "Key events" column. This happens because credit is distributed across multiple interactions. Once you’ve chosen your model, it’s time to focus on tracking the metrics that matter for your SEO efforts.
Tracking Key SEO Metrics
To effectively measure SEO performance, mark important user actions as key events. Go to Admin > Data display > Events and flag relevant actions like file_download, form_submit, or even custom events such as "product comparison".
GA4 automatically tracks several useful SEO metrics. For instance, organic users and sessions help you see how many visitors arrive via organic search. Metrics like engagement rate (calculated as engaged sessions divided by total sessions) and average engagement time give insights into traffic quality and whether visitors find your content engaging. An engaged session is defined as one that lasts over 10 seconds, includes a key event, or involves two or more page views.
Since GA4 doesn’t include keyword data in its standard reports, you’ll need to integrate Google Search Console to access organic search queries. To do this, go to Admin > Product Links > Search Console Links. Once connected, you’ll be able to track metrics like organic impressions, clicks, click-through rate, and average ranking position directly alongside your GA4 data.
Analyzing SEO Performance with GA4 Reports
GA4 reports provide a clear picture of how organic search contributes to conversions, offering insights into SEO's role throughout the customer journey.
Using the Model Comparison Report
The Model Comparison report is a powerful tool for assessing how different attribution models distribute credit to organic search for conversions. You can access it by navigating to Advertising > Attribution > Model comparison in the left-hand menu. Start by selecting Paid and organic last click as your reference model and Data-driven as the comparison model. Then, filter the data by typing "organic" into the search box. The % change column highlights how conversion credit shifts between models. For example, if the Data-driven model assigns more credit to organic search compared to the Last-click model, it indicates that SEO efforts are driving more impact than a simple final-touch analysis might show.
"Attribution models don't just report results - they influence them." - Dan Taylor, Head of Technical SEO, SALT.agency
You can also toggle between Conversion time (focusing on touchpoints that led to conversions during the selected timeframe) and Interaction time (capturing all touchpoints within that period). GA4's Data-driven attribution evaluates over 50 interaction points to determine how each channel contributes to conversions.
Once you've explored attribution models, take a closer look at traffic source reports to dive deeper into SEO performance.
Understanding Traffic Source Reports
The Traffic Acquisition report builds on attribution insights by breaking down session sources and conversion behavior. To access it, go to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition and filter for "organic". This report uses a session-based approach, attributing conversions to the source that initiated the session. Key metrics include total conversions (Key events), Session key event rate (the percentage of organic sessions that resulted in a conversion), and Total revenue, all of which measure SEO's direct impact.
Engagement metrics like Engaged sessions, Engagement rate, and Average engagement time per session provide additional context about how well organic visitors interact with your content. To identify high-performing entry points, add Landing page + query string as a secondary dimension. This can help pinpoint which pages drive the most organic conversions.
You can also analyze performance by Device category to uncover potential issues. For instance, if mobile users converting through organic search lag behind desktop users, it could signal the need for mobile UX improvements. Keep in mind that Search Console data syncs with GA4 after about 48 hours and includes up to 16 months of historical data.
Integrating Google Search Console with GA4
Bringing together Google Search Console and GA4 creates a powerful combination, merging search query insights with on-site engagement and conversion data. This integration provides a more complete picture of your SEO performance by pairing pre-click data (like search queries and impressions) with post-click metrics (such as conversions and engagement rates).
Benefits of Search Console Integration
When you connect Search Console to GA4, you unlock access to the Queries and Google Organic Search Traffic reports. These reports let you link organic search queries directly to conversions and revenue. For instance, you might discover keywords with high impressions but low click-through rates, signaling an opportunity to improve meta titles and descriptions for better performance.
"Through Google search console data, you can determine what users saw in Google search results before they decided to click on your website." – Himanshu Sharma, Founder, OptimizeSmart
GA4 also offers customizable visualizations, allowing you to blend behavioral metrics like engagement rates and revenue. This makes it easier to spot opportunities, such as pages with strong click-through rates but lower rankings, which could benefit from optimization.
How to Connect Search Console with GA4
To set up the integration, you'll need Editor or Administrator permissions and verified ownership of your property. Follow these steps:
- Go to Admin > Product links > Search Console links in GA4.
- Select your Search Console property and link it to your GA4 web data stream.
- Publish the Search Console collection by navigating to Reports > Library.
Keep in mind that each GA4 web data stream can only connect to one Search Console property. After linking, you'll need to manually publish the Search Console reports. The data will start appearing in GA4 within 48 hours and includes up to 16 months of historical data. If you ever need to change the linked property, you’ll have to delete the existing link and create a new one, as links cannot be edited.
Conclusion
This section ties together the insights explored earlier into actionable steps for refining your SEO strategies.
GA4 attribution steps away from traditional last-click models, leveraging machine learning to allocate credit across all touchpoints in the customer journey. The Data-Driven Attribution model shines a light on touchpoints that often go unnoticed, allowing you to justify investments in long-term SEO efforts that build brand recognition and trust, even if they don't lead to immediate conversions.
"GA4 attribution isn't just a settings tweak - it's a strategic lever that can shape how your entire marketing funnel is valued." – Dan Taylor, Head of Technical SEO, SALT.agency
The integration of GA4 with Google Search Console offers a more complete view of your SEO performance by connecting organic search queries directly to conversions. This connection helps pinpoint which keywords truly drive business outcomes, not just traffic. Additionally, the Model Comparison Tool allows you to experiment with different attribution models, helping you understand how credit is distributed across your organic channels before making a final decision.
While GA4 offers robust insights into user behavior, third-party tools fill in essential gaps like analyzing backlinks and benchmarking competitors. For example, the Top SEO Marketing Directory (https://marketingseodirectory.com) provides a curated list of specialized tools and services - ranging from technical audits to content optimization - that can complement GA4's analytics and help you craft a well-rounded SEO strategy.
To get started, set Data-Driven Attribution as your default model, link Google Search Console, and use custom Explorations to monitor the performance of your organic landing pages. These steps will ensure your SEO efforts are both measurable and impactful.
FAQs
What is the difference between Data-Driven Attribution and rule-based models in GA4?
Data-Driven Attribution in GA4 leverages machine learning to evaluate up to 50 user interactions within a 90-day window. It assigns conversion credit based on the actual influence of each touchpoint, offering a clearer and more precise understanding of how users interact with your site.
On the other hand, rule-based models - like last-click or first-click - use fixed rules to assign credit, ignoring the actual impact of individual interactions. By comparison, Data-Driven Attribution delivers richer insights into user behavior, making it a powerful tool for refining SEO and marketing strategies.
Why should you connect Google Search Console with GA4 for SEO?
Connecting Google Search Console with GA4 is a smart move for SEO. Why? It merges search performance data - like queries, impressions, clicks, CTR, and average position - with on-site behavior metrics. This combination provides a more complete view of how users discover your site through organic search and what they do once they land on it.
With this integrated data, you can pinpoint areas to boost your rankings and fine-tune your site's performance in search results. It’s a powerful way to make better, data-driven decisions for your SEO efforts.
How do I set up Data-Driven Attribution for SEO in Google Analytics 4?
To set up Data-Driven Attribution (DDA) for SEO in Google Analytics 4 (GA4), here’s what you need to do:
- Verify your GA4 setup: Make sure your GA4 property is correctly configured and actively collecting data from your website. This is the foundation for accurate attribution analysis.
- Adjust Attribution Settings: Head to the Admin section in GA4 and change the attribution model to Data-Driven under Attribution Settings. Keep in mind, GA4 requires sufficient data - about 10,000 conversions and 50 user interactions within the last 90 days - to enable this model.
- Set SEO Conversion Goals: Identify key SEO-related actions, such as form submissions or purchases originating from organic search. Mark these actions as Conversions in GA4 to track their impact.
Once everything is set, use attribution reports like Model Comparison and Conversion Paths to see how organic search influences conversions. For deeper insights, you can export your data to BigQuery. This approach gives you a clearer picture of how SEO contributes to your business goals.


